AI and Natural Language Processing Offer New Opportunities for Early Diagnosis of Aging-Related Diseases
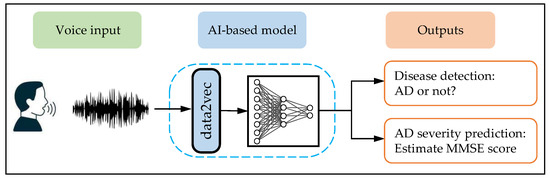
Artificial intelligence (AI) could help improve the early detection of Alzheimer's disease (AD), according to a study by researchers at Drexel University. The study found that OpenAI's GPT-3 AI model could recognize early stages of dementia using spontaneous speech with almost 80% accuracy.
GPT-3, also known as the third generation of OpenAI's General Pretrained Transformer, is an artificial intelligence model that uses a deep learning algorithm to process and analyze large amounts of data. One of GPT-3's key strengths is its ability to perform "zero-data learning," which means it can understand text that would normally require external knowledge that has not been provided.
The researchers used algorithms to identify cues such as hesitation, grammatical and pronunciation errors, and forgetting word meanings. Such features are often used to determine whether patients should undergo a thorough check-up. The researchers trained the model using a large dataset enhanced with speech pattern data needed to identify potential dementia patients. The team plans to create a simple, user-friendly web application for use as a pre-screening tool for dementia at home or in a clinic.
REFERENCE
Agbavor F, Liang H. Predicting dementia from spontaneous speech using large language models. PLOS Digital Health. 2022 Dec 22;1(12):e0000168.



Comments
Post a Comment