Advanced Age is associated with the risk of post-booster COVID-19 death
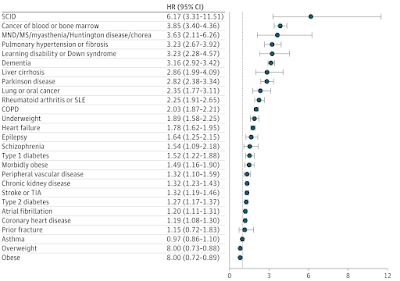
Age was found to be the most important characteristic associated with the risk of post-booster COVID-19 death (panel A) with an HR of 31.3 (95% CI, 26.1-37.6) for an 80-year-old individual compared with a 50-year-old.
Most of the risk groups were associated with an increased HR of post booster breakthrough death, except for congenital heart disease, asthma, and prior fracture. We note that asthma was identified as a risk factor after two doses, while age was not - likely because antibody response studies were focusing on younger cohorts.This study population included those aged 18 to 100 years living in England who had completed both doses of their primary vaccination schedule and had received their mRNA booster 14 days or more prior to December 31, 2021.
REFERENCES
Nafilyan V, Ward IL, Robertson C, Sheikh A, National Core Studies—Immunology Breakthrough Consortium. Evaluation of Risk Factors for Postbooster Omicron COVID-19 Deaths in England. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(9):e2233446. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.33446
Hagiya H, Hikita T, Habu T, Asada M, Yorifuji T, Toyooka S, Otsuka F, Nakayama M. Poor vaccine responsiveness towards third-dose mRNA vaccine of COVID-19 in Japanese older people. Journal of Infection. 2022 Oct 1;85(4):436-80.



Comments
Post a Comment